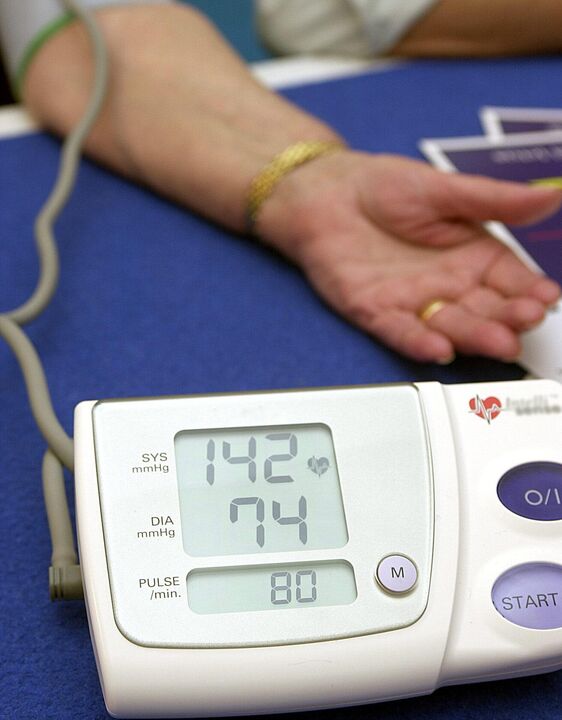
High blood pressure in hypertension is an indicator of persistent chronic hypertension that needs to be treated. Even high blood pressure poses a risk of complications.

The blood pressure level indicates how hard the blood presses on its walls as it moves through the vessels. Blood pressure monitor readings may fluctuate up or down throughout the day. This is considered the norm. But if blood pressure is constantly high, we are talking about a disease called hypertension.
Hypertension, or high blood pressure, leads to serious complications.
The so-called target organs are negatively affected: heart, kidneys, brain, blood vessels, retina. Very often, the consequences of high blood pressure are heart attacks and strokes.
High blood pressure
High blood pressure in hypertension is dangerous and depends on the margin of error. Normal systolic blood pressure ranges from 120 to 129 mmHg and diastolic blood pressure ranges from 80 to 84 mmHg.
The diagnosis of "1st degree hypertension" is made if blood pressure values remain between 140/90 and 160/100 mmHg. This is a mild degree of the disease, in which constantly high blood pressure is not accompanied by damage to internal organs.
In the initial stage of hypertension, blood pressure rises periodically. Constant stress can cause frequent and prolonged surges. With a calm neuropsychic state, periods of increase are short-lived and infrequent.
Persistent high blood pressure in hypertension poses a great threat of developing a hypertensive crisis. It's just a matter of time!
The success of the treatment of high blood pressure directly depends on compliance with the measures and treatment regimen. Strict adherence to the doctor's recommendations will accelerate the decrease in tonometer readings to normal levels. The effect can last a very long time.
You should check your blood pressure if you have the following symptoms:
- headaches in the back of the head (often throbbing);
- dizziness;
- sleep disorders;
- visual effect of "flies";
- Heartache.
The danger of hypertension lies in the fact that its initial stage is often asymptomatic.
A person may not even realize they have high blood pressure. The body quickly adapts to new indicators and the patient feels completely normal. During this time, the pathological process spreads and affects the internal organs.
Catastrophic changes in blood vessels can cause kidney failure, heart attack, stroke, which completely take the patient by surprise.

Lifestyle changes can have a positive effect on blood pressure levels.
To do this, the patient needs:
- ensuring restful sleep;
- avoid stressful situations;
- practice exercises to relax the body;
- dieting;
- increase physical activity.
If these measures fail to cope with high blood pressure, the patient is prescribed medications. The doctor will tell you which medicine is best for normalizing blood pressure after examination.
High pressure
High blood pressure due to hypertension should be treated immediately! The 2nd degree of hypertension (moderate) is characterized by its increase to a level of 160/100 to 180/110 mmHg. To return its indicators to normal at this stage of the disease, the use of medications is necessary. When examining patients diagnosed with stage 2 hypertension, hypertrophy of the left ventricle of the heart is often detected.
Severe hypertension is diagnosed when there is a persistent increase in blood pressure above 180/110 mmHg. Such high levels are usually accompanied by serious complications such as strokes, heart attacks and kidney dysfunction.
High blood pressure due to hypertension is the most common cause of death and disability.

Symptoms of very high blood pressure and severe hypertension include:
- Cardiac arrythmia;
- nosebleeds;
- pain in the heart region;
- headache;
- disruption of gait and coordination of movements;
- severe visual impairment;
- muscular weakness;
- paralysis (due to impaired cerebral circulation);
- coughing up blood;
- inability to self-serve;
- speech disorder;
- disturbance of consciousness.
To treat severe hypertension, strong medications are prescribed or the doses of usual medications are increased. Patients with chronic pathology take pills for the rest of their lives.
Prevention of hypertension
If you haven't yet been diagnosed with hypertension, lowering your blood pressure to normal levels should be a daily goal.
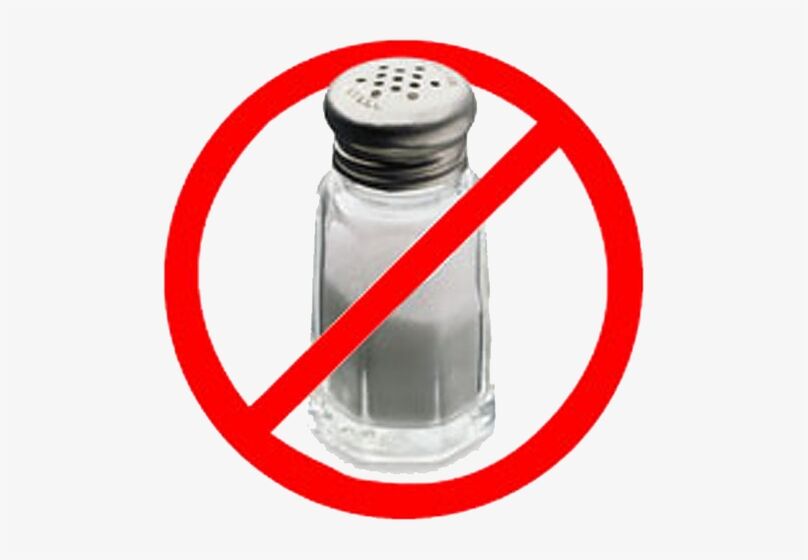

To maintain normal levels, you need to follow a few simple rules:
- maintain normal body weight;
- eat less salt;
- maintain a regime of moderate physical activity;
- stop smoking and reduce the consumption of alcoholic beverages;
- consume foods containing potassium (the average daily requirement is 3, 500 mg of potassium for an adult);
- include fresh fruits and vegetables and low-fat dairy products in your daily diet.
Adequate nutrition
In case of high blood pressure, it is necessary to follow the basic principles of nutrition:
- The daily diet should be balanced in terms of protein, fat and carbohydrate content. Daily intake for an adult: proteins - 100 g, fats - 100 g, carbohydrates - 400 g.
- It is necessary to reduce the consumption of light carbohydrates (quickly converted into glucose).
- Reduce the amount of salt you consume.
- Enrich your daily menu with foods rich in vitamins, potassium, magnesium and other beneficial microelements.
- Replace animal fats with vegetable oils.
- Include seafood rich in iodine and fatty acids in your diet.
- Create the right diet: the number of meals per day is 5, the last meal takes place 2 hours before bedtime.
- Favor boiled or steamed dishes.
- Daily fluid intake should not exceed 1. 5 liters (including liquid dishes and tea).
If there are no chronic abnormalities or vascular diseases, such simple measures should be enough to normalize blood pressure.
For stage 1 hypertension, it is necessary to limit the consumption of certain foods. For levels 2 and 3 - exclude completely.

Hypertensive patients are strictly not recommended to include in their diet:
- rich fish and meat broths;
- fatty pork and lamb meat;
- strong coffee and tea;
- beef fat, lard;
- hot spices;
- baked goods, cakes, pastries;
- salted and marinated vegetables, radishes;
- mayonnaise, fatty sauces;
- chocolate, cocoa;
- sweet soda;
- alcohol and tobacco.
Products that reduce blood pressure
For hypertensive patients, the greatest benefit will come from products containing antioxidants and capable of breaking down fats, thinning the blood and preventing the formation of blood clots.
| Nutrient content of products | Example of product list |
|---|---|
| Folic acid | Tomatoes, spinach, citrus fruits, peas, beans |
| Lactic acid | Sauerkraut, low-fat fermented milk products |
| Vitamin C | Rose hips, garlic, currants, lemon |
| Coarse fiber | Potatoes, cereals, vegetables, herbs, berries and fruits |
| Phosphorus, magnesium, potassium | Nuts, seafood, seeds |
The list of products can be expanded by adhering to the basic principles of creating a menu for hypertensive patients.
Blood pressure changes throughout the day. Particularly strong fluctuations are observed in hypertensive patients. In the morning it is low, then it increases after meals and decreases again. In the evening, blood pressure is significantly higher than in the morning. And at night during sleep, in patients with high blood pressure, it can drop sharply. These flare-ups are more severe than in healthy people.
Normalizing blood pressure in cases of hypertension can save a person's life and protect them from a heart attack or stroke.